UHMW vs Delrin: How to Choose the Right Plastic for Wear, Tolerance, and Load Conditions

UHMW vs Delrin is a decision that shapes wear life, tolerance control, and load performance in real applications. Engineers and buyers must evaluate UHMW vs Delrin when durability competes with precision at the design table.
UHMW survives abrasion, impact, and sliding abuse.
Delrin delivers tight tolerances, stiffness, and repeatable machining.
Choosing wrong costs uptime, accuracy, or both.
UHMW vs Delrin: Side-by-Side Engineering Comparison
Performance summary table
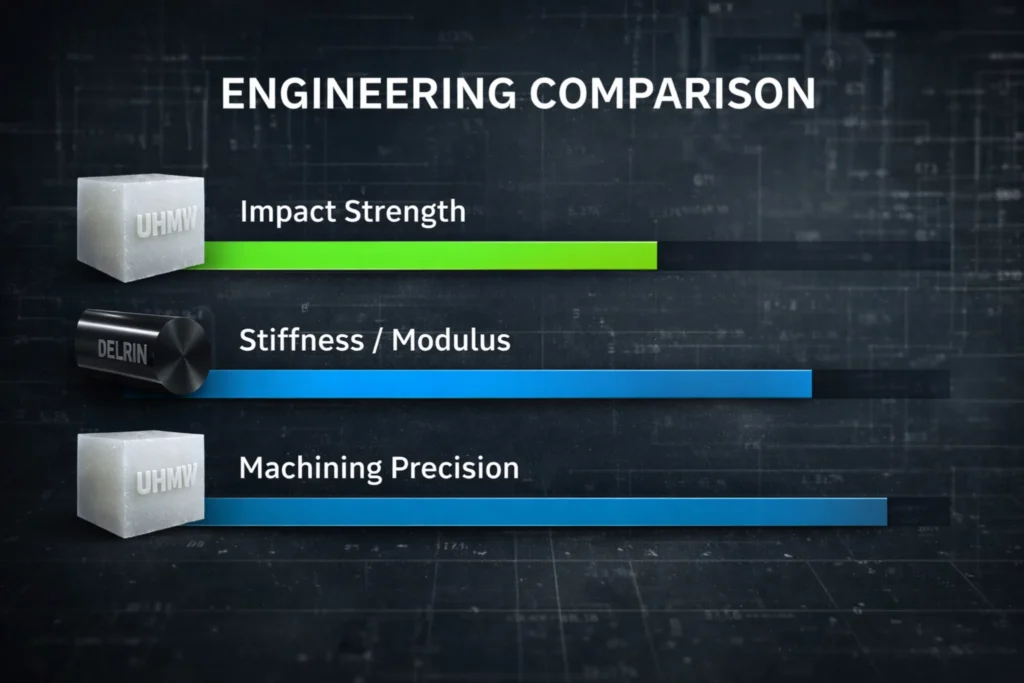
This table compresses the critical engineering differences between UHMW and Delrin, focusing on properties that directly affect wear life, dimensional stability, thermal limits, and friction behavior in moving or load-bearing components.
| Property | UHMW | Delrin (Acetal) |
| Density | ~0.93 g/cm³ | ~1.41 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | ~20–40 MPa | ~60–70 MPa |
| Coefficient of Friction (CoF) | ~0.10–0.20 | ~0.20–0.35 |
| Max Operating Temp | ~82–90 °C | ~90–105 °C |
| Water Absorption | ~0.01% | ~0.2–0.9% |
Design trade-offs at a glance
- UHMW Win: Abrasion, impact resistance, and low-friction sliding under contamination; Loss: poor stiffness and weak tolerance retention under load.
- Delrin Win: High stiffness, strength, and precision machining; Loss: faster wear in abrasive or dirty environments.
- UHMW Win: Moisture immunity and chemical resistance; Loss: creep under sustained load.
- Delrin Win: Structural load handling and repeatability; Loss: higher friction and sensitivity to moisture.
What Performance Problem Are You Trying to Solve?
Friction and sliding wear requirements
Choose UHMW when surfaces slide continuously, pick up grit, or run dry. Its wax-like surface sheds debris and protects mating parts.
Delrin suits intermittent motion with cleaner contact zones. Friction matters less than surface damage here.
Sliding abuse favors UHMW. Controlled motion with predictable contact favors Delrin.
Load type: static vs dynamic stress
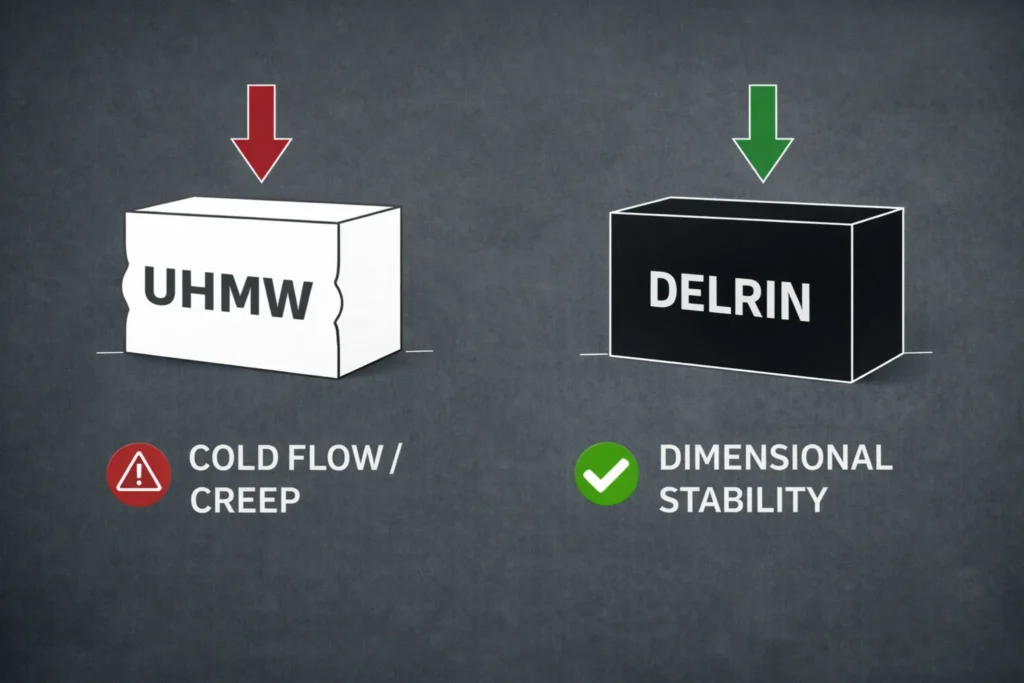
UHMW performs well under dynamic impact but collapses under sustained static load. Constant weight causes creep, cold flow, and permanent deformation. Shelving, rollers, and guides survive; structural supports fail.
Delrin carries static loads with confidence. Its stiffness resists deformation and preserves geometry under compression over time.
Tolerance sensitivity and dimensional control
Tight tolerances expose UHMW’s weakness fast. Expect ±0.010 in or worse as load, temperature, or time increase. Parts grow, slump, or distort.
Delrin holds ±0.001–0.003 in reliably. Precision assemblies, press fits, and alignment-critical components demand Delrin. UHMW introduces risk when accuracy matters.
Material Structure Differences That Affect Real-World Performance
UHMW molecular weight and chain entanglement
UHMW consists of long-chain polymers with extreme molecular weight. These chains tangle densely, dispersing impact energy instead of cracking. Energy absorption defines its performance. Abrasion resistance improves, friction drops, and failure turns ductile. This structure sacrifices stiffness and dimensional control under sustained load.
Delrin crystalline structure and stiffness
Delrin is a highly crystalline homopolymer with tightly packed molecular regions. Crystallinity drives stiffness, strength, and elastic recovery. Loads transfer efficiently through the structure. Parts resist creep, hold shape, and respond predictably to stress. This rigidity supports precision and repeatable mechanical performance.
How structure directly impacts machining and stability
UHMW machines with a waxy, smear-prone behavior that relaxes after cutting. Dimensions drift.
Delrin cuts cleanly with crystalline chip formation. Edges stay sharp, holes stay round, and tolerances remain stable. Structure controls machining confidence and long-term part accuracy.
Mechanical Performance Comparison Under Load
Compressive strength and creep resistance
Under compression, UHMW tolerates short-term loads around 3,000–4,000 psi but deforms as time extends. Creep accelerates once stress exceeds 1,500–2,000 psi in continuous service.
Delrin sustains 8,000–11,000 psi with minimal creep, even under constant load. Its modulus resists molecular movement, preserving geometry.
Use UHMW for shock and sliding, not load holding. Use Delrin when parts must support weight, maintain thickness, and return to shape after unloading. Load duration, not peak force, decides failure.
Impact resistance and fatigue behavior
UHMW dominates impact metrics. Notched Izod impact often registers “no break,” even at low temperatures. Energy dissipates through chain motion rather than fracture.
Delrin records roughly 0.7–1.0 ft-lb/in notched Izod, reflecting stiffness over toughness. Fatigue favors Delrin under cyclic stress within elastic limits.
UHMW survives repeated impacts but loses shape under repeated loading. Impact severity and cycle frequency dictate the winner.
Long-term deformation risks in continuous service
- Permanent thickness loss: Parts flatten, neck, or dish under load, even without visible cracking, signaling cold flow onset.
- Hole and slot distortion: Fasteners loosen as UHMW creeps away from contact points, shifting alignment and increasing wear.
- Fit degradation over time: Press fits relax, guides wander, and assemblies lose positional accuracy despite unchanged external loads.
Friction, Wear, and Sliding Behavior
Coefficient of friction in dry and lubricated systems
UHMW runs at roughly 0.15 coefficient of friction in dry contact, dropping further when moisture or lubrication appears. It self-lubricates through surface transfer.
Delrin averages near 0.25 dry, relying on external lubrication to compete. Under oil or grease, the gap narrows, but UHMW still slides easier. Lower friction reduces heat, noise, and mating-part wear in continuous motion.
Abrasive wear resistance in high-cycle motion
In conveyor rails exposed to grit, sand, or food fines, UHMW outlasts Delrin by multiples. Abrasives embed into UHMW’s surface and stop cutting.
Delrin keeps particles at the interface, accelerating wear. Field cases show UHMW guides running years with surface polishing while Delrin rails require frequent replacement.
Dirty motion environments reward sacrificial toughness over hardness.
Stick-slip performance in precision assemblies
Stick-slip causes chatter, vibration, and positioning errors. UHMW’s soft surface deforms, then releases unevenly under low-speed motion.
Delrin solves this problem. Its stiffness and uniform crystalline structure maintain consistent friction forces. Motion stays smooth, predictable, and quiet.
Precision slides, lead nut carriers, and positioning systems depend on Delrin to eliminate micro-binding.
Machining Accuracy and Manufacturing Control
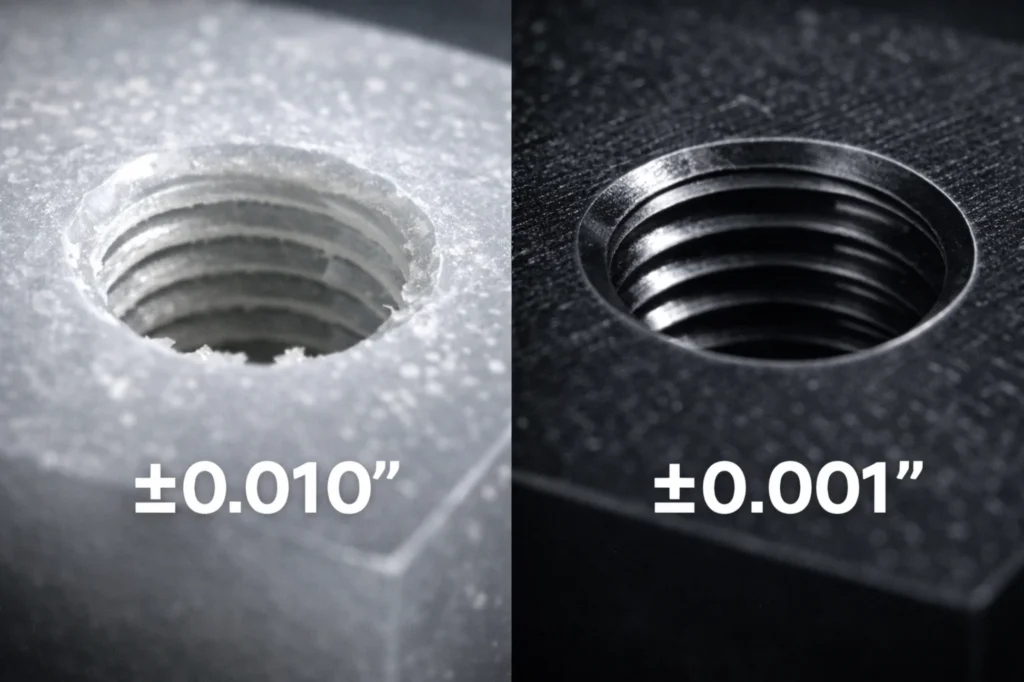

Tolerances achievable with UHMW
- Expect ±0.010 in or looser on most features.
- Use high spindle speeds with light passes to limit heat buildup.
- Sharp tools and aggressive chip evacuation reduce smearing.
- Rough, rest, then finish-cut to manage relaxation.
UHMW machines for fit, not precision.
Dimensional stability advantages of Delrin
Delrin holds shape after cutting. Post-cut relaxation stays minimal because internal stresses remain low. Parts come off the machine close to final size and stay there. Shops routinely achieve ±0.001–0.003 in without secondary operations. This stability supports press fits, threaded features, and multi-axis assemblies where repeatability matters.
Post-machining movement and stress relaxation
UHMW expands roughly 8–10× more than Delrin with temperature change. Heat from cutting triggers movement after machining stops. Parts warp, grow, or shrink as stresses release.
Delrin’s lower thermal expansion limits this risk. Ignoring expansion coefficients invites tolerance drift, scrap, and assembly misalignment.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance Comparison
Moisture absorption and dimensional change
UHMW absorbs roughly 0.01% moisture, producing negligible dimensional change even in washdown or submerged service.
Delrin absorbs about 0.2%, enough to shift tight tolerances and affect fits. Humid or wet environments magnify this gap.
UHMW stays dimensionally indifferent to water. Delrin demands allowance planning when moisture exposure exists.
Chemical compatibility limits

✅ UHMW: Strong acids, strong bases, solvents
❌ UHMW: Oxidizing acids
✅ Delrin: Fuels, oils, mild solvents
❌ Delrin: Strong acids, strong bases
Outdoor, UV, and temperature exposure behavior
Standard UHMW and Delrin degrade under UV. Black, UV-stabilized grades extend outdoor life significantly.
UHMW tolerates cold better and resists impact in freezing temperatures.
Delrin handles moderate heat better but embrittles faster in prolonged outdoor exposure without stabilization.
Cost, Availability, and Supply Considerations
Material cost vs lifecycle cost
UHMW costs less per pound, but lifecycle ROI depends on failure mode. In wear-driven systems, UHMW reduces replacements and downtime.
In precision assemblies, Delrin prevents scrap, rework, and performance loss.
Upfront price misleads. Application-driven longevity defines true cost efficiency.
Sheet, rod, and custom form availability
Both materials ship globally in sheet and rod. UHMW offers thicker slabs and larger profiles. Delrin availability tightens faster in large diameters and custom colors.
Waste, scrap rate, and rework implications
UHMW increases scrap through post-machining movement and tolerance drift. Shops chase size with repeat cuts.
Delrin machines predictably, reducing rework and inspection failures. Stable parts lower waste, speed throughput, and protect margins in precision manufacturing.
Typical Applications Where Each Material Performs Best
UHMW applications where Delrin fails
- Marine fender pads, dock bumpers, and rub strips absorbing impact and saltwater exposure
- Bulk material chutes and liners handling rock, grain, or scrap with constant abrasion
- Conveyor wear strips running dry with contamination
- Snowplow edges and wear shoes exposed to cold and impact
- Packaging guides in washdown environments
- Agricultural liners resisting mud, sand, and fertilizer
Delrin cracks, wears rapidly, or loses service life in these abuse-driven, dirty, sliding applications.
Delrin applications where UHMW fails
- Precision gears requiring tooth accuracy and load transfer
- Fuel system components demanding stiffness and chemical stability
- Valves and seats needing dimensional repeatability
- Bushings under static or sustained compressive load
- Bearing cages with tight clearances
- Electrical and mechanical housings requiring structural rigidity
UHMW creeps, distorts, and loses alignment in these load-bearing, tolerance-sensitive roles.
High-risk misapplication scenarios
CRITICAL WARNING: The number one failure mode is using UHMW as a structural load-bearing part. Cold flow destroys geometry silently. Parts appear intact while tolerances collapse. Assemblies drift, fasteners loosen, and failures propagate without visible cracks. Design intent fails long before catastrophic breakage occurs.
Final Selection: UHMW or Delrin Based on Your Use Case
Choose UHMW if your priority is wear and impact
Choose UHMW when abrasion, impact, and sliding dominate failure risk. It survives grit, shock, moisture, and neglect. Accept loose tolerances and creep in exchange for extreme wear life and toughness.
Choose Delrin if your priority is precision and stiffness
Choose Delrin when geometry, load retention, and repeatability define success. It machines clean, holds tolerances, and resists creep. Trade impact toughness for structural reliability and controlled motion.
FAQs
Which is better for boat trailer bunks or marine slides?
UHMW is the superior choice for marine environments. It has near-zero water absorption (0.01%) and handles the heavy impact of hulls without cracking.
While Delrin is stiffer, it can embrittle with prolonged saltwater exposure and has higher friction, potentially marring the boat’s gel coat.
Can you machine Delrin to tighter tolerances than UHMW?
Yes. Delrin is the industry standard for precision plastic machining, reliably holding tolerances of ±0.001 to ±0.005 inches.
UHMW is prone to “smearing” during cutting and suffers from significant post-machining stress relaxation, often resulting in dimensional drift of ±0.010 inches or more.
Is Delrin or UHMW better for high-temperature applications?
Delrin offers a higher thermal ceiling, with a melting point near 347°F (175°C) and a continuous service temperature up to 180°F-200°F.
UHMW softens significantly above 180°F (82°C) and has a much higher coefficient of linear thermal expansion, causing parts to warp or grow as they heat up.
Why does UHMW seem to last longer in abrasive environments?
UHMW has a unique “sacrificial” surface. Because it is lower in hardness than Delrin, abrasive particles (like sand or grit) embed into the UHMW surface rather than cutting it.
In contrast, Delrin’s hard, crystalline surface keeps grit at the interface, which acts like sandpaper and accelerates the wear of both the plastic and the mating metal part.
Which material should I use for food processing equipment?
Both materials are available in FDA and USDA-compliant grades. However, UHMW is usually preferred for high-wear components like conveyor guides and star wheels because it resists the harsh chemicals used in daily washdowns.
Delrin is preferred for precision food-packaging mechanical parts where dimensional repeatability is critical for the machine’s timing.
